Pure Competition lets many businesses share the same market, lowering the entrance and exit barrier.
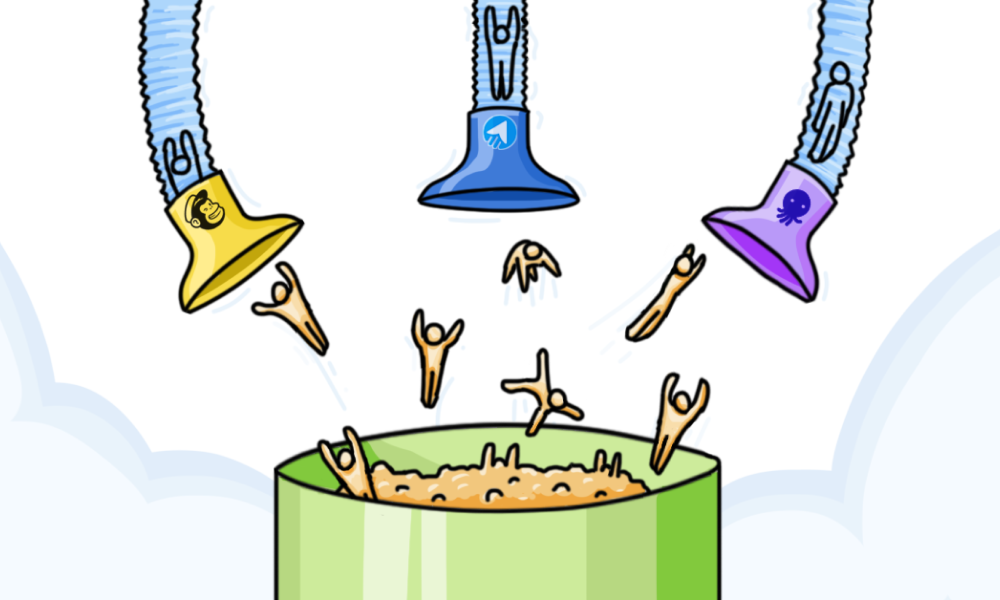
For example, there are several email marketing tools in the current market, like MailChimp, MailBluster, and Email Octopus, which are worth mentioning here. They all provide similar services, assisting businesses and marketers in sending advertising emails to the targeted audiences. The feature photo shows three vacuum cleaners pulling people from a bucket, representing the structure of Pure Competition. The bucket represents the same marketplace, and the three vacuum cleaners are metaphors for different email marketing tools. Different firms generate leads from the same marketplace, providing homogenous services in this marketing structure. It can contain an unlimited amount of competitors with a limited marketplace. The more competitive a market has, the more Competition it will be, affecting the demands and pricing of that particular product.
What is Pure Competition?
Pure Competition is a marketing structure where many firms get themselves involved in competing with each other, offering the same products or services to the same marketplace.
The primary reason this competitive market exists is the standardized and homogenous products or services each firm offers. Besides this, pure Competition allows many businesses to enter and exit this marketplace at the lowest costs. If the entrance and exit points were hard and over costly, then there wouldn’t be a pure competitive marketing structure. Instead, it would be the Monopoly market structure where a particular firm becomes dominant, owning the maximum share of the whole market. The customers of that specific product or service have accurate information about the marketplace that takes the Competition to the highest level.
In a purely competitive market structure, suppliers can’t influence the product price as each firm has a tiny share of the whole market. Suppose one firm raises its product price on its own. In that case, the customers will switch to another competitor, lowering the firm’s profit margin.
Pure Competition is a market structure where any firm can quickly join with their homogenous products, sharing the same market and having no control over the pricing structure.

Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Influencing Pure Competition
The first unit of an economic good satisfies the consumers most, and the law of diminishing marginal utility proves it. In contrast, the second product does it less than the first, and so on.
The first bottle will carry the most value if a hungry man buys two water bottles to quench his thirst. After having the first one, the consumer might think to have a bath with the second one or save it for himself to drink later. It indicates that the second bottle doesn’t have an immediate use value, diminishing the marginal utility compared to the first.
The law of diminishing marginal utility concentrates on decreasing the product value over time. Simply put, marginal utility is consumers’ additional satisfaction by using one more unit of a product. Let’s assume you own two motorbikes. The first has a marginal utility of 50, and the second contains only 10. In that case, the diminishing marginal utility for the second bike would be 40.
Economic goods’ highest availability can lead the marginal utility score to zero or even lower than that. In a purely competitive market structure, the availability of a particular product is high as many firms compete with each other daily.
Example
Imagine three companies supplying mango juice: A, B, and C. If you purchase the juice from A first and then from B and C, the first (A) will contain the most value, diminishing the second (B) and third (C). After drinking the first one, you will not feel that craving for the juice you had while purchasing, resulting in less satisfaction for the second (B) compared to the first (A). Pure Competition pushes businesses to rank their particular product in the first place because they know only this position can satisfy the customers most. It matters the most when customers feel completely satisfied. It goes without saying that consumers are the best marketers when they review positively, enabling the firms to run testimonial advertising.
How to Survive in a Purely Competitive Market Structure?
The best thing about pure Competition is that there is a constant demand for a particular product. The market enables the consumer to know the correct information about the industry, preventing firms from controlling the pricing. Thus, firms face a highly competitive environment that forces them to struggle to survive. There are practices to remain in this competition.
1Higher Economic Profit in the Short Run
If the price increases, the firms tend to increase production for a higher profit in the short run. It is hard to keep that profit margin for as long as people might change their habits with that particular product and find alternatives because of the extra costs. It would be best to pick that opportunity when the market increases the price of the product to increase the company’s capital. Though, there are ways to adapt the customers to the increased costs with price increase letters.
2Reducing Costs by Producing More Units at a Time
More production for the product at a time can reduce the average costs, resulting in a comparatively higher profit. Suppose you own a bakery firm, and bread is one of the products you produce daily. Baking 100 pieces of bread will be costly compared to 500 at a time, resulting in less profit for your company. In that case, you need to improve your sales funnel to collect more orders to produce more units of bread.
3Reducing Costs through Using Technologies
The products and pricing are the same in the purely competitive market structure. It is hard to find extra profit in that situation unless lowering the production costs and selling that product at the market price. Innovation and technology can help you with it, reducing labor and saving time, resulting in more production of the units. If you need 20 employees in your bakery firm without modern equipment, five employees might be alright with those types of machinery. It will not only decrease the costs but also save time with the production.
4Ensuring the Highest Marginal Utility
Pure Competition ensures the highest availability of a product and producing firms. It lets consumers know the information about the market, as stated before. If you buy two bottles of water from different firms, the first one will quench your thirst, containing the highest marginal utility. The second one might help you wash or drink more and save for later use, but quenching your thirst will satisfy you the most. Marginal utility measures the satisfaction of the consumers. The more satisfied your customers are, the more positive impression your business will have. The best way to survive in Pure Competition is to convince customers to pick your product for immediate use to understand its highest value.
5Adding or Removing Features
Features that measure the overall value of a product or service can be updated to maintain the elasticity of market demand. Although MailBluster and Mailchimp provide email marketing services and also share the same marketplace, they have uniquenesses in their offerings. When MailChimp adds more features to charge its customers with the highest costs, MailBluster offers the most essential elements of email marketing at the lowest cost. As a result, the business owners who want to save money or the starters choose MailBluster to survive in the Pure Competition.
If the lowest pricing can bring you the highest marginal utility (consumer satisfaction), then why won’t you use MailBluster to drive your essential email marketing campaign? This tool will let you send 3,000 marketing emails for free without any kinds of hidden cost.










 Contents
Contents
